Intro
Google's SearchLiaison recently announced the initiation of their Site Reputation Abuse enforcement, which took effect on May 6th. The enforcement will initially focus on manual actions, with algorithmic measures to follow later. In response to this update, many websites have already removed pages hosting third-party content aimed at influencing search engine rankings.
Manual Actions First, Algorithmic Later
SearchLiaison emphasized that manual reviews are currently being conducted to identify sites in violation of the policy, with automated algorithmic actions to be implemented soon. In manual reviews, Google employees assess whether a website warrants removal from the search index due to policy violations.
Understanding Site Reputation Abuse
A classic yet revived tactic involves marketers piggybacking on other websites to increase their own content's search engine rankings. This strategy, often referred to as "parasite SEO," inaccurately implies that the host website is exploited without permission. In reality, marketers often collaborate with website owners to boost rankings consensually.
This method isn't limited to small-time marketers but is also practiced by major brands, especially in credit card promotions and product reviews.
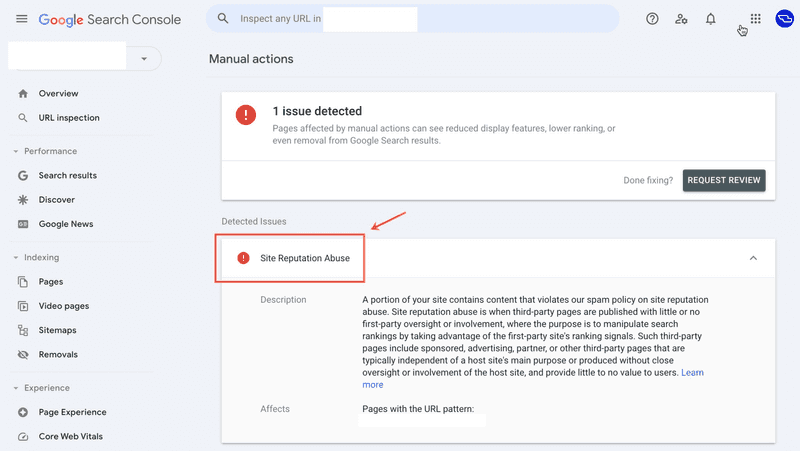
Google's Focus on Third-Party Content
The Site Reputation Abuse policy specifically targets websites that host third-party content with little involvement or oversight. Google's definition states that this kind of abuse occurs when third-party pages are published primarily to manipulate search rankings by leveraging the host site's ranking signals. Such pages include sponsored, advertising, partner, or other third-party content not aligned with the host site's main purpose and providing limited user value.
Brodie Clark, an independent SEO consultant, highlighted Google's recent rollout of manual actions targeting "site reputation abuse," warning that an algorithmic component will follow. This initiative directly confronts the practice known as "Parasite SEO," which aims to manipulate search rankings by publishing third-party pages with minimal oversight.
 Source: Linkedin
Source: Linkedin
Google's notification outlines that "site reputation abuse" involves third-party pages exploiting the host site's ranking signals with little to no oversight. Examples include:
-
Educational Site: A third-party review page on payday loans that is redistributed to other websites.
-
Medical Site: A page about "best casinos," unrelated to the medical site's primary focus.
-
Movie Review Site: Pages on unrelated topics like social media follower buying, confusing users and manipulating rankings.
-
Sports Site: A third-party page on workout supplement reviews with no staff involvement.
-
News Site: Coupons provided by a third party aimed at manipulating search rankings.
Clark emphasizes that if a site fits any of these scenarios or has received a manual action notice, it should take immediate steps to comply with Google's guidelines.
Policy Enforcement Update
Google's SearchLiaison tweeted confirmation that enforcement has started:
“It’ll be starting later today. While the policy began yesterday, the enforcement is really kicking off today.”
The All-in-One Platform for Effective SEO
Behind every successful business is a strong SEO campaign. But with countless optimization tools and techniques out there to choose from, it can be hard to know where to start. Well, fear no more, cause I've got just the thing to help. Presenting the Ranktracker all-in-one platform for effective SEO
We have finally opened registration to Ranktracker absolutely free!
Create a free accountOr Sign in using your credentials
In response, major brand websites have recently taken down sections hosting reviews with questionable credibility. The removed reviews often lacked original photos, specific measurements, or tangible testing results.

