Intro
Google's ambitious new vision for online search, powered by AI technology, has sparked a significant backlash over concerns it could undermine the internet's open ecosystem. At the heart of this controversy are Google's newly launched "AI Overviews," which are generated summaries designed to answer search queries by pulling information from across the web.
AI Overviews and Legal Challenges
AI overviews appear prominently at the top of search results pages, potentially reducing users' need to click through to publishers' websites. This feature has led to legal action in France, where publishers accused Google of violating intellectual property rights by using their content to train AI models without permission.
In April 2024, a group of French publishers won an early court battle, with a judge ordering Google to negotiate fair compensation for repurposing snippets of their content. Publishers in the US are raising similar objections, arguing that Google's AI overviews unfairly profit from others' content and threaten to siphon traffic away from original sources.
Concerns From Publishers
Industry watchers highlight that AI overviews could impact millions of independent creators who rely on Google Search referral traffic. Frank Pine, executive editor at MediaNews Group, compares Google's approach to plagiarism, stating, "If journalists did that to each other, we’d call that plagiarism."
Kimber Matherne, a food blogger, expressed concerns that Google's AI overviews might disservice the world by cutting out the content creators who are the lifeblood of information. Raptive, an ad services firm, estimates that these changes could lead to $2 billion in lost revenue for online creators, with some websites potentially losing two-thirds of their search traffic.
Concerns From Industry Professionals
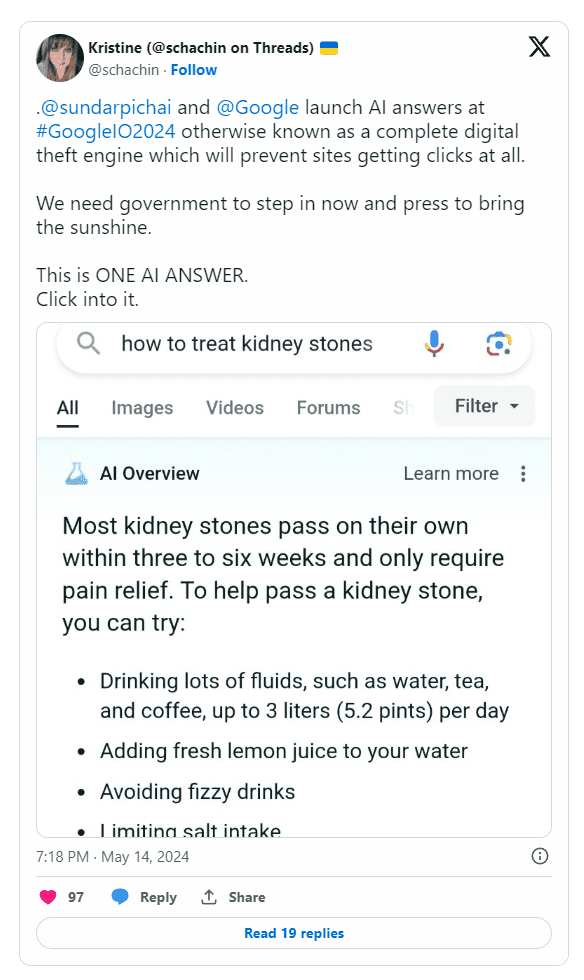
Google's AI overviews have drawn sharp criticism from industry professionals. Matt Gibbs criticized Google for developing its AI knowledge base by "ripping off" publishers who did the actual work to create the knowledge. Kristine Schachinger described Google's AI answers as "a complete digital theft engine" that prevents sites from getting clicks.
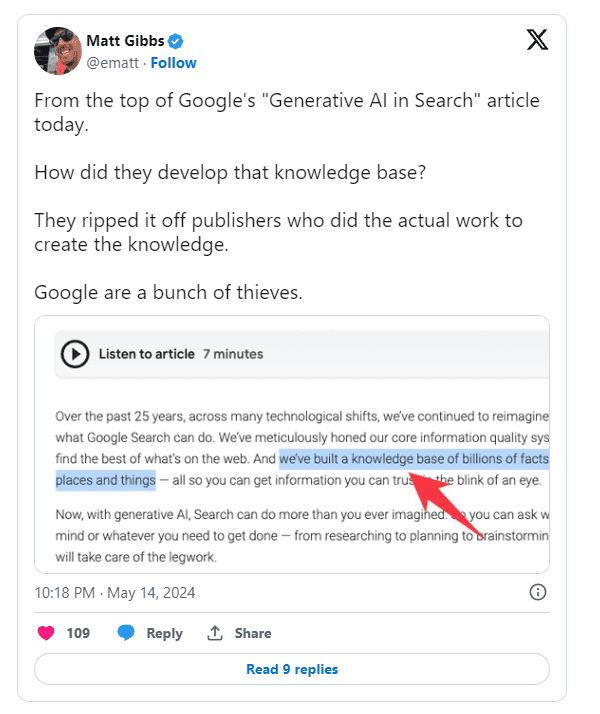
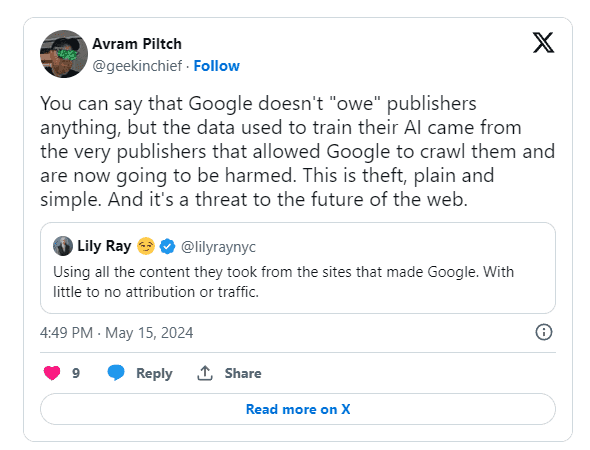
Gareth Boyd highlighted the struggles of blogger Jake Boly, whose site experienced a 96% drop in Google traffic, stating that the precedent set by OpenAI and Google is "scary" and amounts to "open theft of content." Avram Piltch echoed these sentiments, accusing Google of theft and warning that this practice threatens the future of the web.
The All-in-One Platform for Effective SEO
Behind every successful business is a strong SEO campaign. But with countless optimization tools and techniques out there to choose from, it can be hard to know where to start. Well, fear no more, cause I've got just the thing to help. Presenting the Ranktracker all-in-one platform for effective SEO
We have finally opened registration to Ranktracker absolutely free!
Create a free accountOr Sign in using your credentials

Legal Gray Area
This controversy delves into broader debates around intellectual property and fair use, as AI systems are trained on vast amounts of data scraped from the internet. Google maintains that its models only use publicly available web data and that publishers benefit from search traffic. However, current laws weren't designed with AI training in mind, creating a legal gray area.
The Path Forward
This debate underscores the need for updated rules on how AI uses online data. Some suggest revenue sharing or licensing fees when publisher content is used to train AI models. Others propose an opt-in system that gives website owners more control over their content's use for AI training. The French court rulings indicate that, without explicit guidelines and good-faith negotiations, courts may need to intervene.
Conclusion
The balance between search engines and content creators has been pivotal to the web's value. As AI technologies evolve, ensuring this balance with new safeguards is crucial to maintaining the open exchange of information that makes the internet so valuable.

